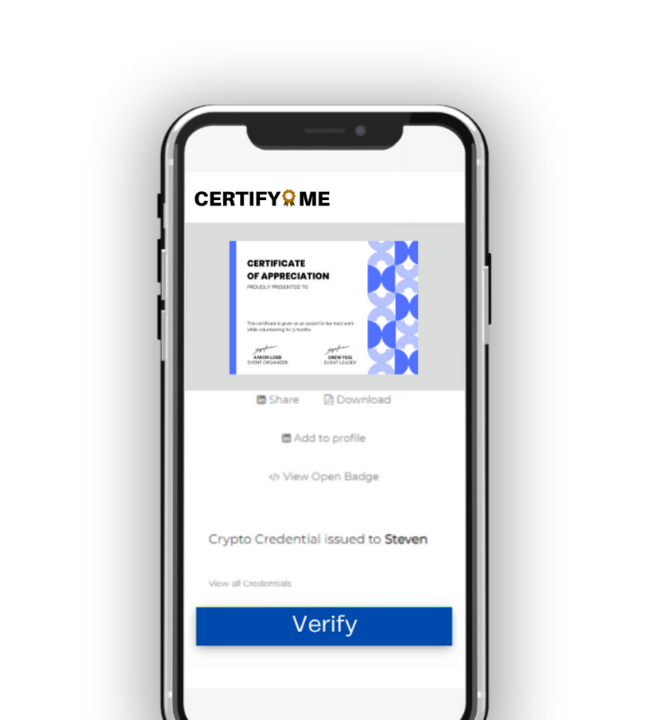
Which is better paper or digital certificates?
People still prefer physical or paper certification, despite the incorporation of digital documentation, records, and processes. This could be because organisations are still utilising outdated methods, or because people are unable to access or get familiar with digital processes and documents. Regardless of which option is chosen, digitization is a requirement for the future. So, let’s talk about which is better: Is it better to have paper or digital certificates?
The Argument:
For Paper Certifications: Paper certificates have been used as identification documents, legal documents, educational records, and many other things for decades. It was, at times, the most reliable method of confirming our identification and the validity of the document’s criteria. Although it is the most extensively used documentation, it does have significant drawbacks.
Paper certificates, often known as tangible certificates, are difficult to keep track of and store. Not to mention that they are fragile, prone to damage, and easily lost or stolen. In the event of a loss or damage, the procedure involved running errands for documentation and verification, and it was found to be thorough.
For Digital Certificates: Digital certificates, on the other hand, are electronic documentation of an individual’s competency in a certain qualification, as well as identifying documents and legal records. Blockchain technology is used to issue digital certificates, which stores and records certificate data in their digital databases. This eliminates the risk of data manipulation or credential loss, and it can be saved and shared on digital platforms for public viewing.
Digital certificates are encrypted and frequently come with a passcode or digital key that protects the document from unauthorised access and cyber risks. Since they are also backed by meta-data verification of the document is easy and hassle-free.
Digital Certificates: Benefits
Secure:
As previously stated, the most secure method of issuing a digital credential is through the use of digital certificates. Many digital credentialing platforms include blockchain technology, which makes the issuing process easier while still providing bank-level security. To protect the document from unauthorised or third-party access, digital certificates can be encrypted, often with a digital password or key. They are protected from cyber dangers such as data tampering, forgery, and duplication, as well as hacking.
Verified:
Digital credential comes with meta-data that stores the name of the issuer, recipient and criteria of the certificate along with issue date and expiration date into the digital databases or digital data. These databases help track the issuing of the credential and also aids in verifying the legitimacy of the document.
Shareable:
One of the main advantages of digital certificates is their flexibility to be shared. When a person receives a digital certificate, they are routed to a sharing page where they can distribute it on digital platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, as well as social-networking sites like LinkedIn and via mail. Additionally, digital certificates include a URL or link that can be included in their portfolios or resumes.
Cost-effective:
Paper certification, which includes the costs of manufacturing, storage, and labour, is expensive and time-consuming. Digital credential platforms, on the other hand, can enable businesses and organisations to develop and issue digital certificates at a low cost, saving time and effort. Because the digital credential platform comes with its own set of design templates and interactions, it saves firms money on certificate creation.
Integration and Automation:
Unlike physical certificates, which need a lot of human effort to issue, share, and create, digital credentials are connected with LMS and are automated, saving a lot of time and effort. Immediate responses and certification delivery to candidates are also aided through automation. Quick access to design tools is facilitated by design integrated software.
What about folks who can’t utilise or access digital certificates and would rather have paper certificates?
That’s the thing about digital certificates: they can be printed into a tangible form, which could aid those who don’t know anything about digital credentials. All that is required is to download the certification, print the documents, and obtain the certification’s physical record.
In Conclusion:
Despite the fact that paper certificates have been around for decades and are more commonly used than digital certificates, people must address the growing digitalisation and demand for digital certificates, since digital credentials are the future of documentation and recording identification.

 Author :
Author :