Digital Badging in K-12 Education: A New Approach to Assessment
One promising solution that has gained momentum in recent years is the use of digital badging in K-12 education. Digital badging offers a novel approach to assessment, recognizing and motivating students for their achievements in a way that goes beyond traditional grades.
The Anatomy of a Digital Badge
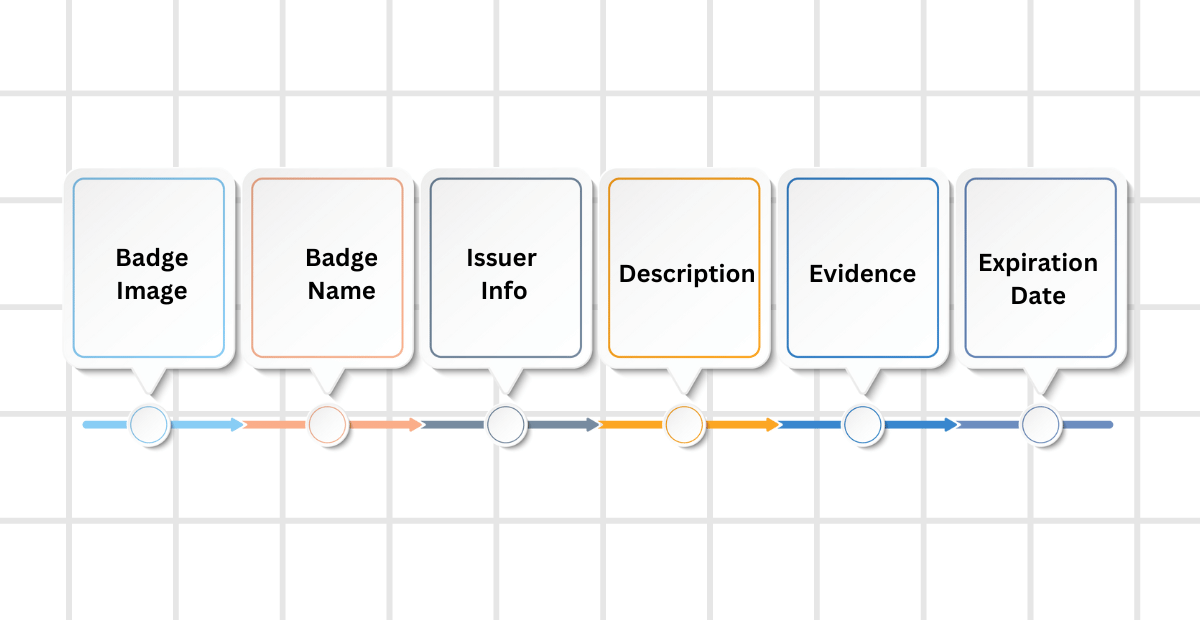
A typical digital badge comprises several key elements:
-
Badge Image: This is the visual representation of the badge, often featuring an appealing design related to the achievement it represents.
-
Badge Name: A clear and concise title that describes the achievement or skill.
-
Issuer Information: Details about the organization or institution that has issued the badge, ensuring credibility and authenticity.
-
Description: A brief description of the criteria or requirements that the recipient met to earn the badge.
-
Evidence: Links or references to specific artifacts, projects, or assessments that demonstrate the recipient’s achievement.
-
Expiration Date: In some cases, badges may have an expiration date to indicate the currency of the achievement.
In K-12 education, digital badges are typically awarded by educators or institutions to students who have demonstrated specific skills or achievements. These badges can cover a wide range of areas, from academic subjects like mathematics and science to broader competencies like leadership, creativity, and critical thinking. To earn a digital badge, students must meet predefined criteria, which can include completing coursework, passing assessments, or participating in extracurricular activities.
Once a student earns a digital badge, they can add it to their digital portfolio or share it on social media platforms, creating a visible record of their accomplishments. This aspect of digital badges contributes significantly to their effectiveness in motivating students, as we will discuss in more detail later in this article.
The Benefits of Digital Badging in K-12 Education
-
A Holistic Assessment Approach
One of the most significant advantages of digital badging is its ability to provide a more holistic assessment of students’ skills and achievements. Unlike traditional grading systems that primarily focus on test scores and GPA, digital badges allow educators to recognize and reward a broader range of talents and competencies. This holistic approach acknowledges that students excel in various areas, both inside and outside the classroom. -
Personalized Learning Paths
Digital badging encourages personalized learning paths for students. Since badges can be earned in specific subject areas or skill sets, students have the flexibility to choose their learning goals and pursue their interests. This personalization fosters a sense of ownership over their education, increasing their motivation to learn and excel. -
Motivating Students
Motivating students to actively engage in their education is a perpetual challenge for educators. Digital badging addresses this issue by tapping into the psychology of motivation. When students see a tangible reward in the form of a digital badge for their efforts, they are more likely to stay engaged, set goals, and strive for excellence. This is particularly important in K-12 education, where building a strong foundation for lifelong learning is a key objective. -
Fostering a Growth Mindset
Digital badges promote a growth mindset by emphasizing the value of effort and improvement. When students earn badges for meeting specific criteria or mastering new skills, they internalize the idea that learning is an ongoing process. This mindset shift can have a profound impact on students’ attitudes toward education, leading them to embrace challenges and persevere in the face of setbacks.
Implementing Digital Badging in K-12 Education
-
Setting Clear Criteria
To effectively implement digital badging in K-12 education, it is essential to establish clear and transparent criteria for earning badges. Educators should define the specific skills, competencies, or achievements that each badge represents. This clarity ensures that students understand what is expected of them and what they need to do to earn a badge. -
Aligning with Curriculum
Digital badges should be closely aligned with the curriculum to ensure they enhance the educational experience. Educators can integrate badges into lesson plans, projects, and assessments, making them an integral part of the learning process. This alignment helps students see the relevance of badges to their education and encourages active participation. -
Encouraging Student Choice
To promote student engagement and motivation, educators should offer a variety of badges representing different subjects and skills. Giving students the freedom to choose which badges they want to pursue empowers them to take ownership of their learning journey. Additionally, educators can provide guidance and support to help students set realistic goals and track their progress. -
Providing Feedback and Support
Feedback plays a crucial role in the digital badging process. Educators should provide constructive feedback to help students improve their skills and work toward earning badges. This feedback loop fosters a growth mindset and encourages students to view challenges as opportunities for growth. -
Recognizing Non-Academic Achievements
Digital badges are not limited to academic achievements. K-12 educators can also use them to recognize and reward non-academic accomplishments, such as leadership, teamwork, community service, and creativity. This inclusive approach acknowledges the diverse talents and contributions of all students.
Successful Implementation of Digital Badging
-
Case Study 1: Gamifying Language Learning
In a language learning program for middle school students, digital badges were used to gamify the learning experience. Students earned badges for completing language modules, achieving specific proficiency levels, and participating in cultural exchange activities. This approach not only motivated students to actively engage in language learning but also provided a visual representation of their progress. -
Case Study 2: STEM Enrichment Program
A STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) enrichment program in a high school used digital badges to recognize students’ achievements in STEM-related projects and competitions. Students earned badges for designing innovative solutions, participating in robotics competitions, and conducting scientific research. The badges served as a testament to their dedication to STEM education and encouraged them to pursue STEM careers. -
Case Study 3: Character Education
An elementary school implemented digital badging to promote character education and social-emotional learning. Students earned badges for demonstrating qualities such as empathy, respect, and responsibility. These badges not only reinforced positive behaviors but also helped create a school culture focused on character development and well-being.
Overcoming Challenges and Concerns
-
Ensuring Equity
One of the primary concerns with digital badging in K-12 education is ensuring equity. To address this challenge, educators must provide equal access to opportunities for all students to earn badges. This may involve offering additional support to students who face barriers to achievement, such as those with disabilities or those from disadvantaged backgrounds. -
Validating Badges
The credibility and validity of digital badges are essential. To address concerns about the authenticity of badges, educators should ensure that badges are issued by reputable sources and that the criteria for earning them are well-defined and transparent. Collaboration with industry professionals and higher education institutions can also enhance the recognition of badges. -
Balancing Assessments
Digital badges should complement, not replace, traditional assessments. It’s important to strike a balance between badges and traditional grading systems to ensure that students receive a comprehensive evaluation of their academic performance. Badges can focus on specific skills and competencies, while grades provide an overall assessment. -
Privacy and Data Security
Collecting and storing data related to digital badges raises privacy and data security concerns. Educators must implement robust data protection measures to safeguard students’ personal information. Transparency in data collection and usage is crucial to building trust with students and their families.
Future Directions and Trends
-
Integration with Blockchain Technology
One emerging trend is the integration of blockchain technology with digital badging. Blockchain offers a secure and tamper-proof way to verify the authenticity of digital badges. This development could enhance the credibility of badges and make them more widely accepted in higher education and the job market. -
Cross-Institutional Recognition
Efforts are underway to establish cross-institutional recognition of digital badges. This means that badges earned in K-12 education can carry over into higher education and the workforce. As this recognition network expands, the value of digital badges will increase, providing students with a more seamless educational pathway. -
Adaptive Learning Systems
The use of digital badges can be integrated into adaptive learning systems. These systems tailor educational experiences to individual students based on their performance and goals. Digital badges can serve as milestones within these systems, guiding students toward their desired outcomes. -
Enhanced Analytics
As the use of digital badges grows, so does the potential for collecting and analyzing data on student achievement and engagement. Advanced analytics can provide educators with valuable insights into student learning trends and areas where additional support may be needed.
Conclusion
Digital badging is ushering in a new era of assessment in K-12 education. By recognizing and motivating students for their achievements, digital badges offer a more holistic and personalized approach to assessment. They foster a growth mindset, encourage active engagement, and empower students to take ownership of their learning journey. While challenges such as equity and data security must be addressed, the benefits of digital badging are clear. As the educational landscape continues to evolve, digital badges are poised to play a central role in shaping the future of assessment and learning in K-12 education.

 Author :
Author :