A certificate of completion and a digital badge serve different purposes. While one marks a major milestone, the other one highlights a smaller, skill-based achievement.
A certificate of completion is used when someone finishes an entire course, program, or required training and needs formal proof of completion. A digital badge is used to recognise a specific skill or capability and is designed to be easy to verify and share online. Simply put, certificates are best for formal completion, while badges are better for skill recognition and visibility.
So, when it comes to recognizing someone for their achievement, how will you choose the right one?
| Aspect | Certificate of Completion | Digital Badge |
| What it represents | Confirms that a learner has completed a full course, program, or required training. | Confirms that a learner has earned a specific skill or achieved a defined outcome. |
| Typical learning size | Long, structured learning such as degrees, diplomas, or full courses. | Short or focused learning such as modules, assessments, or skill units. |
| Primary goal | Formal proof of completion. | Proof of skill or capability. |
| How it is presented | A document (digital PDF or printed) with written details. | A visual badge with clickable, embedded data. |
| How verification works | Verified by checking the document or contacting the issuer. | Verified instantly through a public verification page. |
| What is verified | That the program or course was completed. | Who earned the badge, who issued it, and what criteria were met. |
| Skill visibility | Skills are usually described in text, if at all. | Skills are clearly highlighted and easy to understand. |
| Sharing method | Shared as a file or link. | Shared with one click to platforms like LinkedIn. |
| Expiration handling | Usually permanent. | Often time-bound or renewable. |
| Best suited for | Academic records, compliance, formal recognition. | Skill signalling, ongoing learning, professional visibility. |
What is a Certificate of Completion?
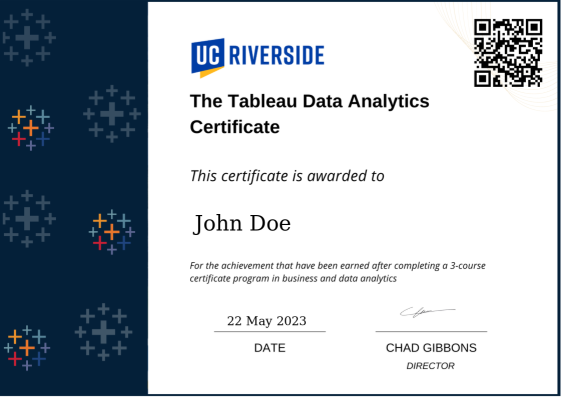
A certificate of completion is a formal document issued when a learner finishes a full course, program, or required learning activity.
You’ll commonly see certificates used in situations like:
- A university awarding proof after a semester-long course
- A training provider issuing confirmation after compliance training
- An organisation certifying that an employee completed onboarding
In these cases, the key question being answered is: “Did this person complete what was required?”
Certificates usually include basic details such as the learner’s name, the program or course title, the issuing organisation, and the date of completion. Their main purpose is record-keeping and formal proof, not skill display.
Today, many certificates are issued digitally instead of on paper, making them easier to store and share.
If you want to understand how digital credentials work more broadly, this article explains the concept clearly : What is a Digital Credential?
What is a Digital Badge?
.png)
A digital badge is a micro-credential that proves a learner earned a specific skill or achievement, rather than completing an entire program.
For example:
- A student completes an “Advanced Excel” module inside a larger degree
- An employee passes a cybersecurity awareness test
- A professional completes a short tool-specific workshop
Instead of issuing a long certificate each time, a digital badge is awarded for that one skill.
A proper digital badge is not just an image. It contains verifiable data behind it, such as:
- Who issued the badge
- Who earned it
- What had to be done to earn it
- When it was issued
- Whether it expires
Most digital badges follow the Open Badges standard, which ensures that this information can be verified and trusted across platforms.
Common digital badge features include:
- One-click social sharing (for example, to LinkedIn)
- An instant verification page
- Issuer and recipient validation without exposing personal data
- Optional expiration dates for time-sensitive skills
- Optional evidence links such as assessments or projects
Digital badges are designed to make skills easy to see, easy to check, and easy to share.
Using Both Together (A Common Approach)
Many organisations don’t choose one over the other. They use both.
A common setup looks like this:
- One certificate of completion at the end of a full program
- Multiple digital badges along the way for individual skills
This approach gives learners:
- A formal record for completion
- Visible proof of skills they gained during the journey
If you’re also weighing digital formats against traditional paper ones, this comparison might help you decide what fits your organisation best : Paper vs Digital certificates
Conclusion
Certificates of completion and digital badges are not competing tools. They solve different problems.
Certificates are best when completion needs to be formally recorded. Badges are better when skills need to be shown, shared, or verified over time.
Understanding this difference makes it easier to choose the right format for your learners, your organisation, and your long-term credentialing goals.

 Author :
Author : 




